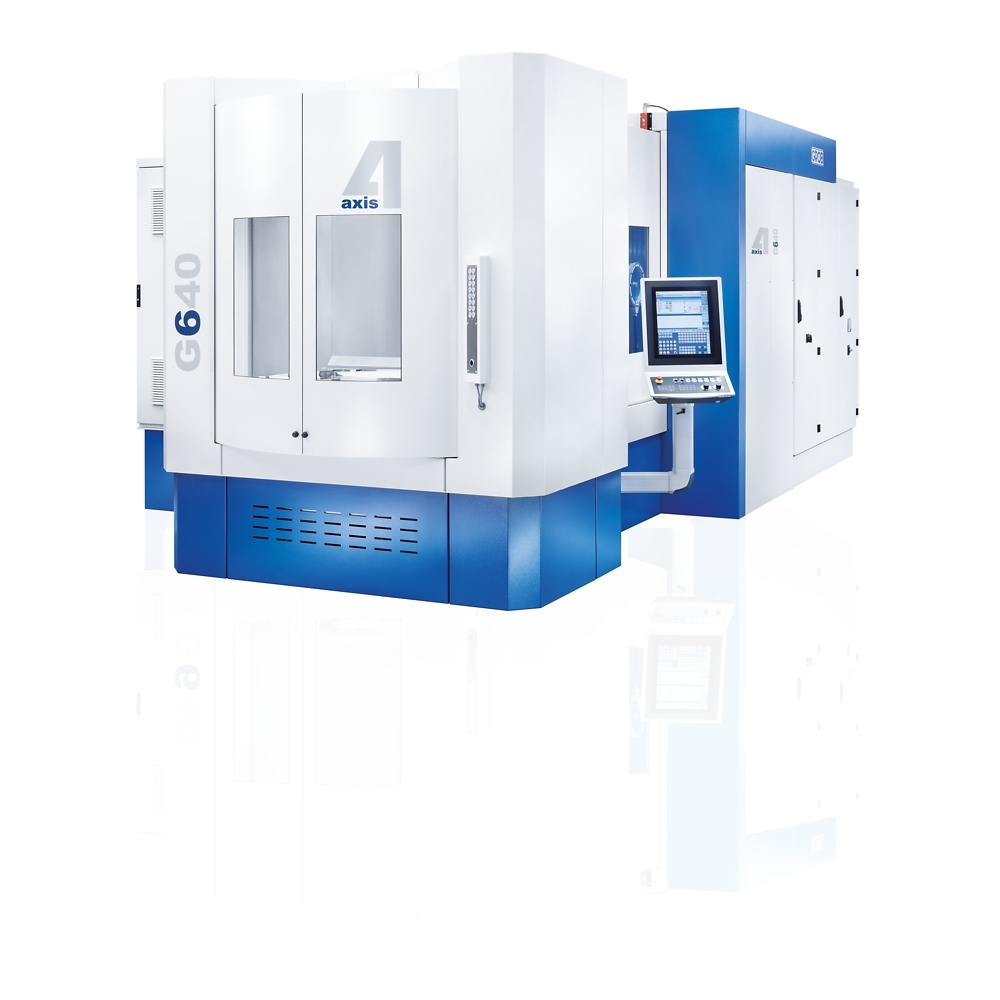
CNC computerized numerical control is a system that allows you to automate machine tools. This method allows machinery to be operated using programmed commands on a computer and is increasingly used in machining workshops thanks to its precision and speed, which allows it to reduce costs and production times.
CNC numerical control in metalworking
CNC numerical control dates back to the 1940s and 1950s and is based on machines that worked by manual numerical control, following commands that were encoded on a punched card microscope. Over the years and with the introduction of analog and digital technologies, the CNC began to evolve to become one of the most widely used methods today.
Thanks to the modification of the processors, the numerical decimal control or computer numerical control or what is the same, CNC numerical control was created. Right now, the CNC is a revolution for the industry, because, in addition to the many advantages it offers, it has also made microprocessors cheaper.
CNC computerized numerical control is based on the use of a computer to control and monitor the movements made by a static or portable machine tool.
CNC machines
More and more machine tools include this technology; thus we can find, for example, lathes, milling machines, grinding machines, laser and water jet cutting machines, as well as presses. The versatility of CNC numerical control allows it to be included in multiple pieces of equipment that facilitate the work of workshops, reduce production costs, increase speed and require minimal human intervention.
The machines that include this technology have an integrated computer that is part of the equipment; Most of these devices have a very sophisticated feedback system that can automate the work, adjust speed, pressure, part position, etc.; without the need to have an operator constantly.
In addition, the CNC works with a sophisticated system of motors and drive components that allow the movement of the axes of the machine along the part to be machined. On the other hand, the machines that work with the CNC numerical control follow a series of commands and instructions that are entered into the computer through the CNC alphanumeric language. Thanks to these indications, and depending on the machine, the equipment can alternate between cutting tools, in order to carry out the work on the part.
How do CNC numerical control machines work?
The operating principle of these machines is very simple, since they require a system of coordinates (commands) that determine the movement that the cutting tool must follow, as well as the angle of inclination of the part (some machines can reposition the piece by itself). The movements are carried out on the coordinate axes of the machine.
How does the tool know where to move? This is achieved thanks to the previous programming that the operator has to do in the alphanumeric language. The machine receives the indications from the computer through the G and M codes; Later, the computer program or software converts these codes into electrical signals that activate the motors and, consequently, the cutting tools.
Components of a CNC machine
A CNC numerical control machine tool has six fundamental parts or elements:
- Machine tool (it is the machine itself, adapted to the technology: lathe, milling machine, etc.).
- input device.
- Controller.
- Drive systems.
- Computer.
- Feedback device, available only on some types of machine tools.
CNC numerical control language
To activate the CNC machine tool, it is necessary to program it using a specific language. This programming can be manual or automatic. In the case of manual programming, this is done when the operator makes reasoning and calculations that will be executed on the part and enters them into the computer.
Automatic programming, on the other hand, is distinguished because the calculations are carried out by the computer, based on a series of data and parameters that the operator supplies; the result is an APT data exchange.
The CNC language is characterized in that it is made up of sets that comprise the same machining phase and are called blocks or sequences. These blocks must contain all the geometric, technological and machine functions to be able to machine. The characters used by the CNC numerical control are governed by the DIN 66024 and 66025 standards, where we find some of these codes:
- N, for the address that corresponds to the block or sequence number and can be programmed up to 1000 (N000 to N999).
- X, Y, Z: Directions of the axes of the machine.
- G, direction followed by the preparatory machining functions. Describes the motion functions of the machine.
- M, direction of auxiliary or complementary functions (rotations, stop, etc.)
- F, forward speed.
- S, main spindle rotation speed .